Secure Wrappers
For security, Lightning Locker restricts the use of global objects by hiding an object or by wrapping it in a secure version of the object. For example, the secure version of window is SecureWindow. Locker intercepts calls to window and uses SecureWindow instead.
To see which APIs are supported by the SecureWindow, SecureDocument, and SecureElement wrappers, use the Locker API Viewer tool.
SecureWindowAvailable: Lightning Web Components and Aura Components
Secure wrapper for the
windowobject, which represents a window containing a DOM document.If a Lightning web component and an Aura component belong to the same namespace, they share the same
SecureWindowinstance.SecureDocumentAvailable: Lightning Web Components and Aura Components
Secure wrapper for the
documentobject, which represents the root node of the HTML document or page. Thedocumentobject is the entry point into the page’s content, which is the DOM tree.If a Lightning web component and an Aura component belong to the same namespace, they share the same
SecureDocumentinstance.SecureObjectAvailable: Lightning Web Components and Aura Components
Secure wrapper for an object that is wrapped by Lightning Locker. When you see a
SecureObject, it typically means that you don’t have access to the underlying object and its properties aren’t available.SecureElementAvailable: Lightning Web Components and Aura Components
Secure wrapper for the
elementobject, which represents various HTML elements.If a Lightning web component and an Aura component belong to the same namespace, they share the same
SecureElementinstance.Lightning web components additionally use the
SecureLightningElementwrapper.SecureLightningElementAvailable: Lightning Web Components
Secure wrapper for the
LightningElementbase class. Lightning web components extend theLightningElementbase class, and at runtime Locker switches the class withSecureLightningElement. When you create a Lightning web component, do not extendSecureLightningElementdirectly.These APIs are not supported.
Element.attachShadow()Element.shadowRoot—usethis.templateinsteadElement.slot
SecureTemplateAvailable: Lightning Web Components
Secure wrapper for the
templateobject, which represents ashadowRootnode.These APIs are not supported.
Node.localNameNode.namespaceURINode.nodeValueNode.nextSiblingNode.previousSiblingNode.parentElementNode.parentNodeNode.prefixNonDocumentTypeChildNode.nextElementSiblingNonDocumentTypeChildNode.previousElementSiblingDocumentOrShadowRoot.getSelection()DocumentOrShadowRoot.pictureInPictureElementDocumentOrShadowRoot.styleSheetsDocumentOrShadowRoot.pointerLockElementDocumentFragment.getElementById()ParentNode.appendParentNode.prependconstructorEventTarget.dispatchEvent
Lightning Web Security doesn't use wrappers. It uses API distortions in JavaScript sandboxes to selectively modify APIs that enable non-secure behaviors.
Let’s look at a sample Aura component that demonstrates some of the secure wrappers.
The c:secureWrappers component creates a <div> HTML element and a lightning:button component.
Here’s the client-side controller that peeks around in the DOM.
We use console.log() to look at the <div> element and the button. The <div> SecureElement is wrapped in a Proxy object as a performance optimization so that its data can be lazily filtered when it’s accessed.
We put a debugger statement in the code so that we could inspect the elements in the browser console.
Type these expressions into the browser console and look at the results.
Here’s the output.
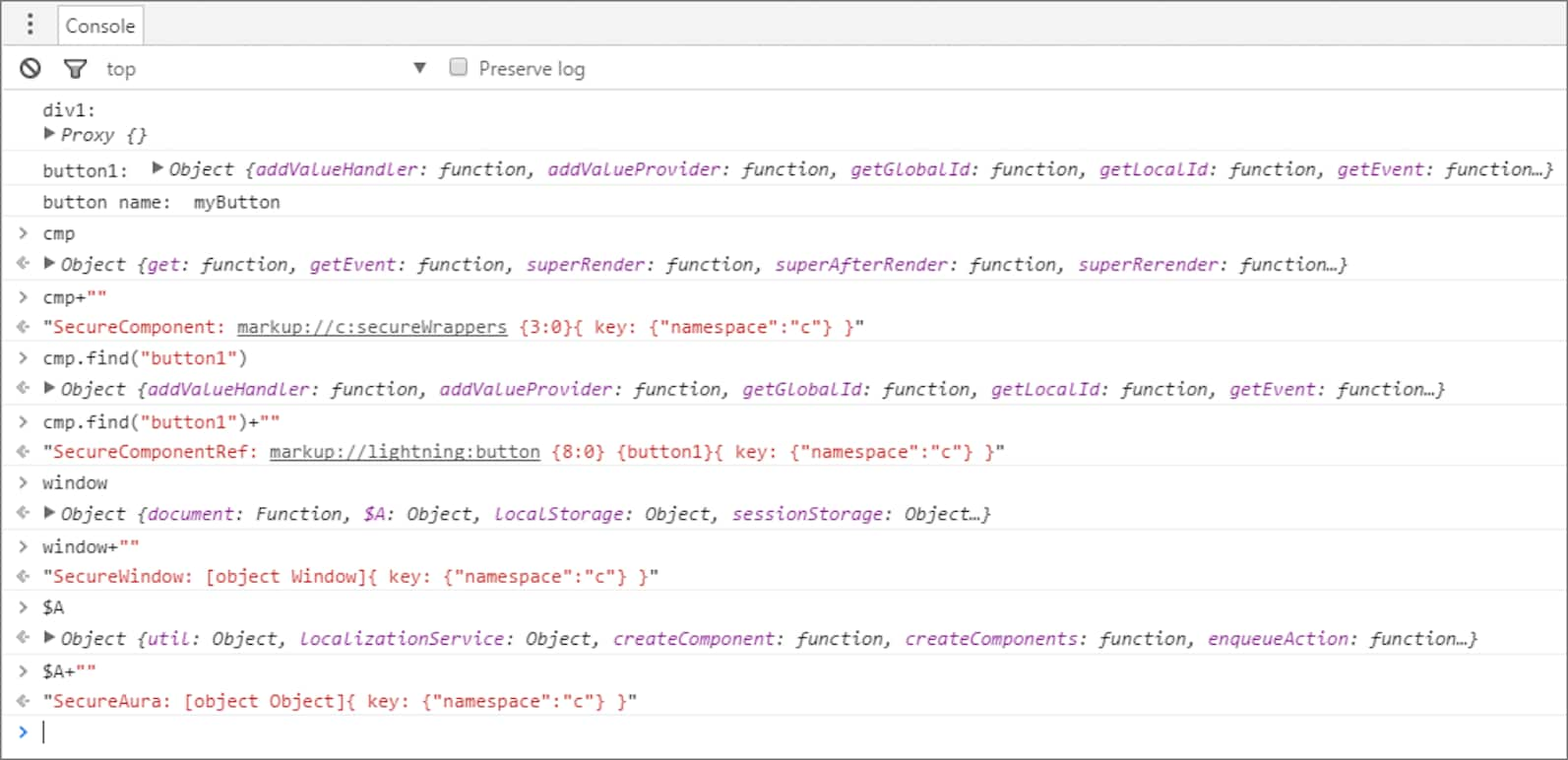
Let’s examine some of the output.
cmp+""returns aSecureComponentobject forcmp, which represents thec:secureWrapperscomponent.cmp.find("button1")+""returns aSecureComponentRef, which represents the external API for a component in a different namespace. In this example, the component islightning:button.window+""returns aSecureWindowobject.$A+""returns aSecureAuraobject.
See Also