Implement Location Messaging on iOS
The MobilePush SDK for iOS uses location capabilities of your customer’s device to trigger location-based notifications. The SDK caches geofence messages and displays them on devices when users cross a geofence boundary. To implement location-based messaging on your app using the MobilePush SDK, you must obtain user permission for location services.
To successfully use this functionality, your Marketing Cloud Engagement admin must enable your account with access to MobilePush and Location Services.
Starting with iOS 14, users have the option to use approximate instead of precise location. Geofences and beacons aren’t triggered for users who provide approximate location permission. See Apple Developer Documentation: Accuracy Authorization.
Location messaging and beacon support in iOS versions 14 and later require precise location authorization. The MobilePush SDK sends only precise location updates to Marketing Cloud, and ignores approximate location data.
If location is enabled in your MobilePush SDK configuration, you can use location messaging by calling a single method. You can enable location in your SDK configuration using the setLocationEnabled method of the PushConfigBuilder class.
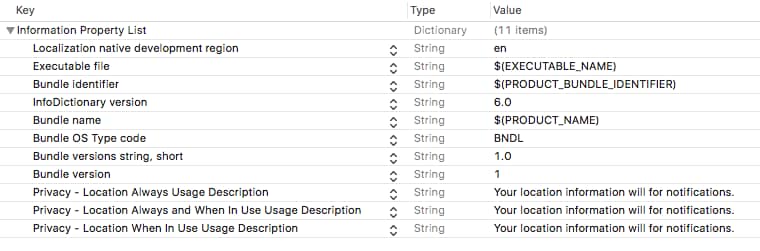
Apple also requires that you add these keys to your Info.plist file to enable location services.
NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescriptionNSLocationAlwaysAndWhenInUseUsageDescriptionNSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription
For more information, see Choosing the Location Services Authorization to Request on Apple’s Developer Documentation site.
The MobilePush SDK requires Always permissions for full geofence and beacon functionality. An application doesn’t receive location messages if an app user selects When-in-use authorization.
When your application is ready to enable location features, including geofence and beacon messaging, call the SDK’s startWatchingLocation method to start watching location. This code example shows how to start watching location using version 10 of the SDK.
For version 8 of the SDK, use this code.
If you use version 7 of the SDK, use this code.
The MarketingCloudSDK+Location.h header file details additional methods to get information about location and control the frameworks behavior.
The SDK suppresses geofence messages with no content. If you include AMPscript or a merge field in your message that returns an empty string, your app doesn’t display that message to the user.
We enable beacon support when you implement the location requirements on this page.
To range for beacons in the background, add an entry to your app’s Info.plist. This permission ensures that your app can range for beacons when your app is in the background or suspended.
The SDK suppresses beacon messages with no content. If you include AMPscript or a merge field in your message that returns an empty string, your app doesn’t display that message to the user.
To understand how beacons behave in different situations, see Beacon Behavior.
If you create your own CLLocationManager object, we can’t guarantee that features of our SDK work as intended.
If you have enabled notifications using MarketingCloudSDK and have called mp.startWatchingLocation(), you can access the device’s last known location using the SDK.
This code example shows how to get the device’s last known location using version 10 of the SDK.
For version 8 of the SDK, use this code.
If you use version 7 of the SDK, use this code.
Normally, the app downloads new regions and messages as the device moves more than 5 kilometers from the last location and download of this data. However, if your app serves users who spend much time within a single 5-kilometer radius, consider adding the ability to do a background refresh of regions and messages. Apple controls when this background refresh takes place. However, Apple also allows the SDK to download new regions and messages for those times your user spends a considerable amount of time in a single 5-kilometer region.
In your Info.plist, implement this key to enable this function. To refresh geofences and beacons, the SDK requires the app to implement the App downloads content from the network mode. This mode gives the app permission to periodically download new regions and messages.
In your Info.plist, add keys under UIBackgroundModes:
fetch: To perform periodic background app refreshes, the App downloads content from the network mode is required.location: To enable location in the SDK and to range for beacons in the background, the App registers for location updates mode is required.
In your application delegate method -application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:, implement this code:
Implement the handler for this functionality in your application delegate class. This code example shows how to implement the handler using version 10 of the SDK.
For version 8 of the SDK, use this code.
If you use version 7 of the SDK, use this code.
See MarketingCloudSDK+Base.h for more information about this method.
You can deliver location messages to a subset of your MobilePush audience by using the MobilePush SDK. When a mobile device breaks a geofence or comes into proximity of a Bluetooth beacon, the SDK triggers a callback to your mobile app. This callback is used to evaluate whether to show the message.
Your app can apply criteria, including information within the MobilePush message itself, to determine whether to show the message. Here are some use cases.
- Show the message if the user’s my store location is within the geofence region.
- Show the message if the user has items in the app shopping cart and if the message has an “abandonedCart”:”true” custom key.
- Show the message only when the store is open based on the app’s store location list and the region and local time.
- Don’t show messages if the user isn’t logged in to the app.
- Show specific messages based on the user’s customer profile. For example, customers who are coffee lovers get messages about coffee, but customers who prefer pastry receive a message to “add a coffee” when they’re in the shop.
This code example shows how to implement location message segmentation using version 10 of the SDK.
For version 8 of the SDK, use this code.
If you use version 7 of the SDK, use this code.