Handle Lightning Out 2.0 App Events
Configure custom events so that embedded components and the host page can communicate with each other.
Lightning Out 2.0 app components load in iframes instead of directly on the host page. To overcome communication restrictions across iframe boundaries, Lightning Out 2.0 wraps custom events in messages using window.postMessage(). This internal implementation allows event listeners on one side of the iframe boundary to detect events dispatched from the other side. From your perspective, events are still created and handled with the standard EventTarget and CustomEvent interfaces.
Recall that a Lightning Out 2.0 app includes Lightning Out 2.0 web components that mirror your embedded LWC components but run in the context of the host page. If you need a refresher, review Understand Lightning Out 2.0 Architecture. This mirroring extends to events.
If you add an event listener to a Lightning Out 2.0 web component, Lightning Out 2.0 also adds the event listener to the corresponding LWC component running in the Salesforce context.
If you dispatch an event from a Lightning Out 2.0 web component, Lightning Out 2.0 also dispatches the event from the corresponding LWC component. When you create a custom event, set the bubbles and composed properties to true so that events can pass through the shadow DOM boundary.
Therefore, if an event is fired inside the Salesforce context, the event can bubble up from the LWC component event listener to the Lightning Out 2.0 web component event listener. Then, the event is handled in the host page context. And similarly, if an event is fired in the host page context, the event can propagate down from the Lightning Out 2.0 web component event listener to the LWC component event listener. Then, the event is handled in the Salesforce context.
Let’s demonstrate Lightning Out 2.0 event handling with some example code.
Here’s a custom Lightning web component called c-card-component, which is a wrapper for the lightning-card component. The card has a lightning-button component that sends a message to the host page when clicked. The card also has a conditional directive that renders a new message card when a user clicks a button on the host page.
Here’s the JavaScript for c-card-component.
The connectedCallback() function runs when the component first loads. It initializes an event listener that responds to the sendMessageToLWC custom event defined on the host page. When the host page dispatches this event, the event listener calls the handleMessageFromHost() event handler. The event handler adds the received message to a list for the c-card-component to display.
c-card-component also has the handleSendMessage event handler, which responds to users clicking the component’s nested lightning-button. The event handler defines and dispatches the lwcMessagetoHost event to the host page.
Now let’s examine the host page. It has three main UI areas relevant to this example: the embedded c-card-component (1), a button that users click to send messages to c-card-component (2), and an area where messages from c-card-component will appear (3).
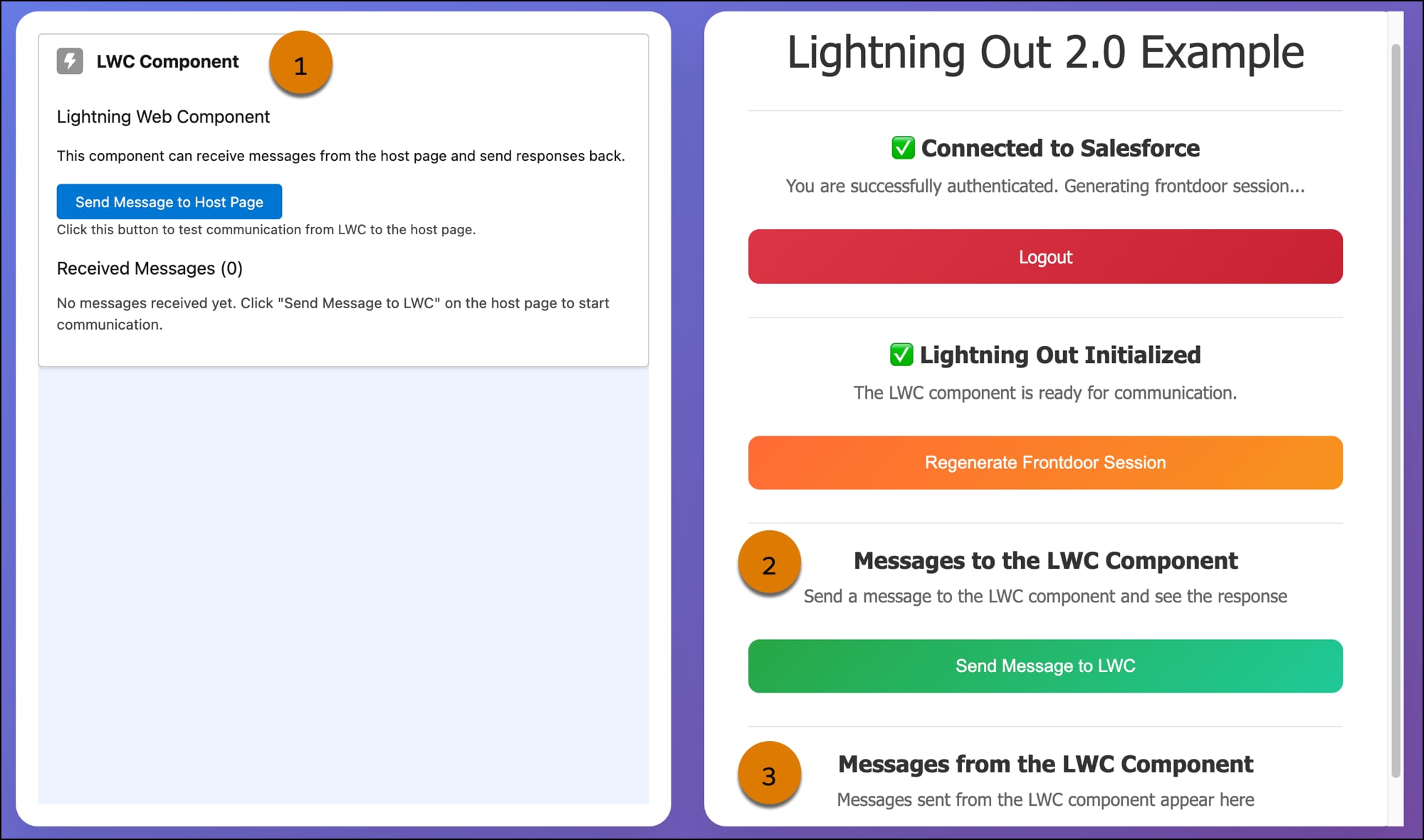
Here’s an HTML snippet of the host page. It includes:
- The Lightning Out 2.0 JavaScript library.
- A Lightning Out 2.0 app with a
c-card-componentweb component. - A
sendMessageButtonbutton that dispatches a custom event toc-card-componentwhen clicked. When the message is dispatched, the host page also shows a confirmation message. - An
lwcMessageResponseelement that shows the latest message that the host page receives from the embeddedc-card-component.
Here’s a snippet of the host page’s script.js file.
To dispatch an event to the embedded c-card-component, an event listener is set on the sendMessageButton button. When a user clicks the button, the event listener calls an anonymous event handler. This event handler defines and dispatches the sendMessageToLWC event directly on the Lightning Out 2.0 web component c-card-component. The event is mirrored to the embedded LWC component c-card-component.
To receive the lwcMessageToHost event from the embedded c-card-component, set an event listener on the Lightning Out 2.0 web component c-card-component. Ensure that the Lightning Out 2.0 app and the c-card-component have loaded before setting this event listener. For example, set the event listener conditionally based on whether the frontdoor-url attribute has been set on the lightning-out-application. When the embedded c-card-component dispatches the lwcMessageToHost event, the event listener calls the handleLwcMessage function. This function displays the latest message from the embedded component on the host page.
To learn how to set the frontdoor URL at run time, see Set Up Authentication for Lightning Out 2.0 in Salesforce Help.
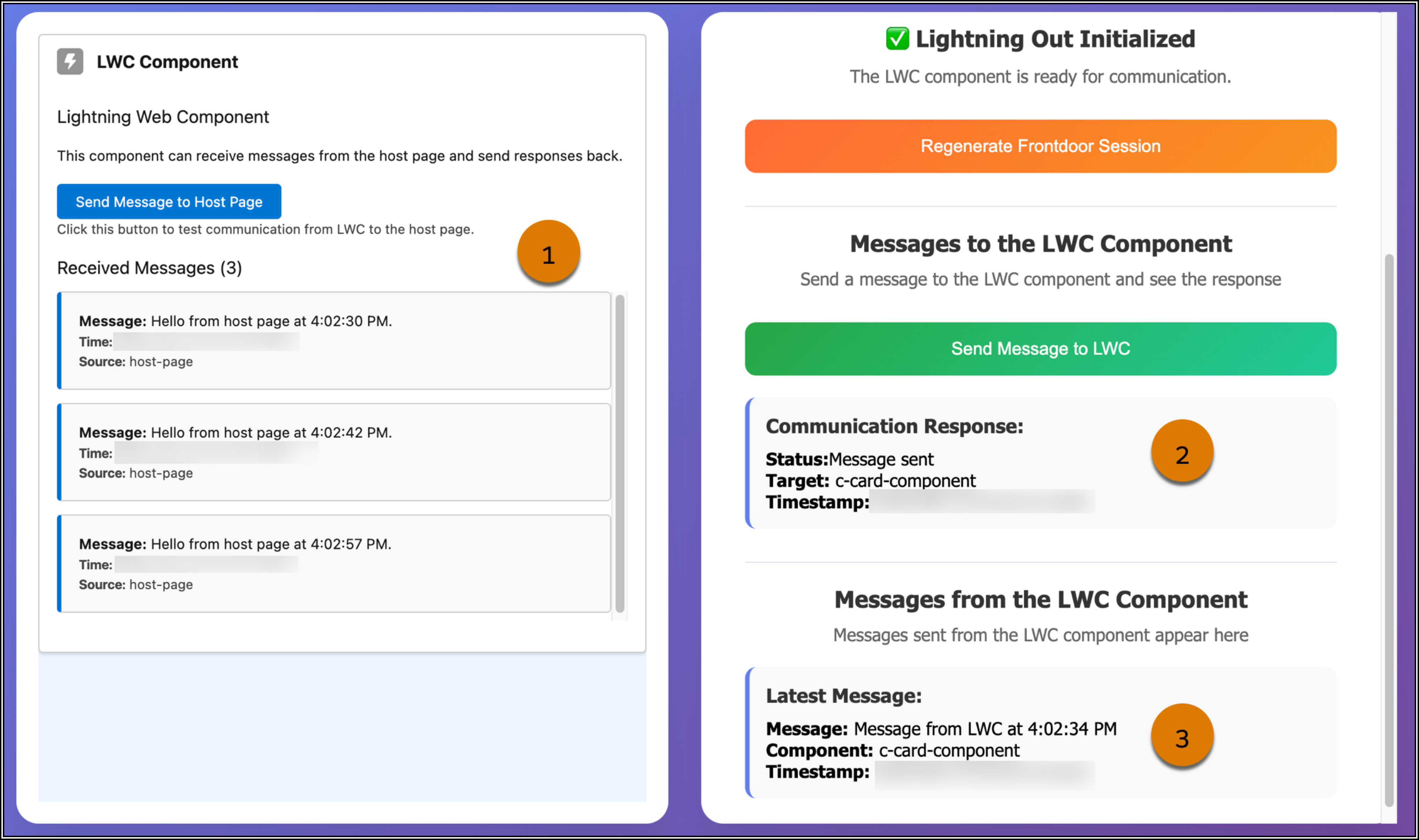
Here’s the host page after a user dispatched three messages from the host page to c-card-component (1). Whenever the user dispatches a message to c-card-component, a confirmation message appears in the Messages to the LWC Component section (2). The user also dispatched messages from c-card-component to the host page. The most recent message appears in the Messages from the LWC Component section (3).
See Also
- Communicate with Events
- Salesforce Help: Set Up Authentication for Lightning Out 2.0