Remote Development (Beta)
Salesforce Extension for VS Code supports remote development and allows you to use a container as a full-featured development environment. You can open a project mounted into a Docker container or use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2 to edit with full code completions, code navigation, debugging, and more.
The remote development feature is currently in beta. If you find any bugs or have feedback, open a GitHub issue.
Refer to VS Code documentation if you want to understand more about remote development:
- Use a Docker container as your development container
- Use WSL 2 as your development container
- Provide full-featured development environment
- Switch your development environment by connecting to a container
Follow these instructions for remote development using a Docker Container.
To start remote development in dev container, install:
- Docker Desktop. For system requirements and installation instructions, see:
- Windows: Currently Docker desktop for windows supports only Linux Containers and not Windows Containers. During the install process, ensure you use the default option of Linux Containers.
- Mac
- Linux
- Latest version of VS Code
- Latest version of VS Code Remote Development Extension Pack.
After you install VS Code and Docker Desktop for your operating system:
- For Windows, set source code locations you want to open in a container. In Docker, right-click and select Settings / Preferences > Shared Drives / File Sharing. See Container tips if you hit trouble with sharing.
- For Linux, see supported platforms. From the terminal, run
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERto add your user to thedockergroup. This setting takes effect after you sign out and back in again.
- Latest version of the Salesforce Extension Pack
-
Open an existing project you want to work with or create a new project.
-
From the Command Palette, run Remote-Containers: Add Development Container Configuration Files. If you are unable to see this command, make sure that you have installed the latest version of VS Code Remote Development Extension Pack.
-
Select Salesforce Project from the list of templates to add
SFDX .devcontainerfolder. The.devcontainerfolder contains thedevcontainer.jsonfile that defines how to configure the dev container, the Dockerfile to use, and the extensions to install.VS Code detects the dev container configuration file and prompts you to reopen the project folder in a container. If the pop-up window disappears, from the Command Palette, run Remote-Containers: Reopen in Container.
VS Code creates a dev container the first time you open the project. After the dev container is built, the project folder in your local system automatically connects and maps to the container, and the side bar shows
Dev Container: Salesforce Project. The container pre-installs and configures Java, Git, Salesforce CLI, and all other extensions defined in thedevcontainer.jsonfile.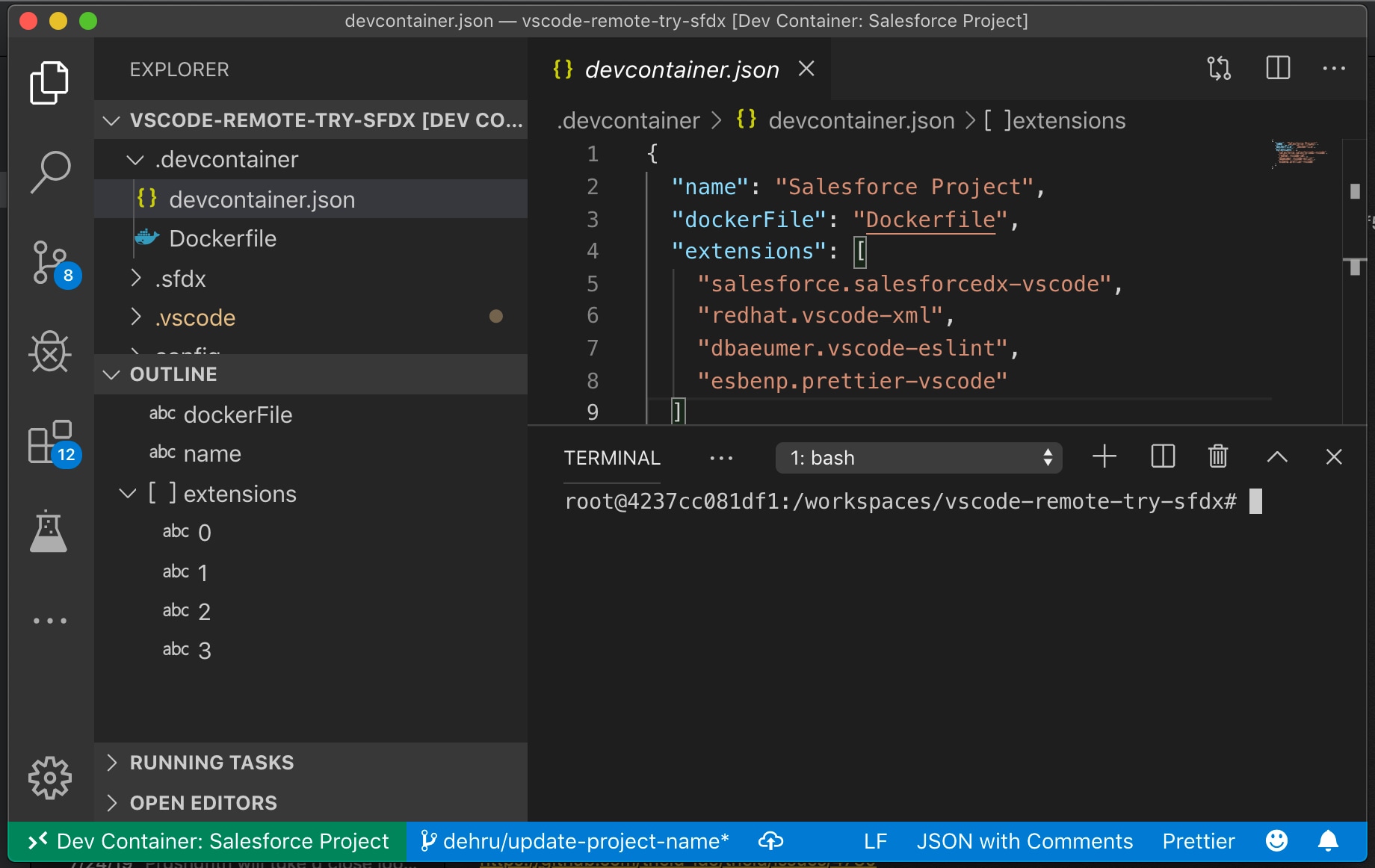
-
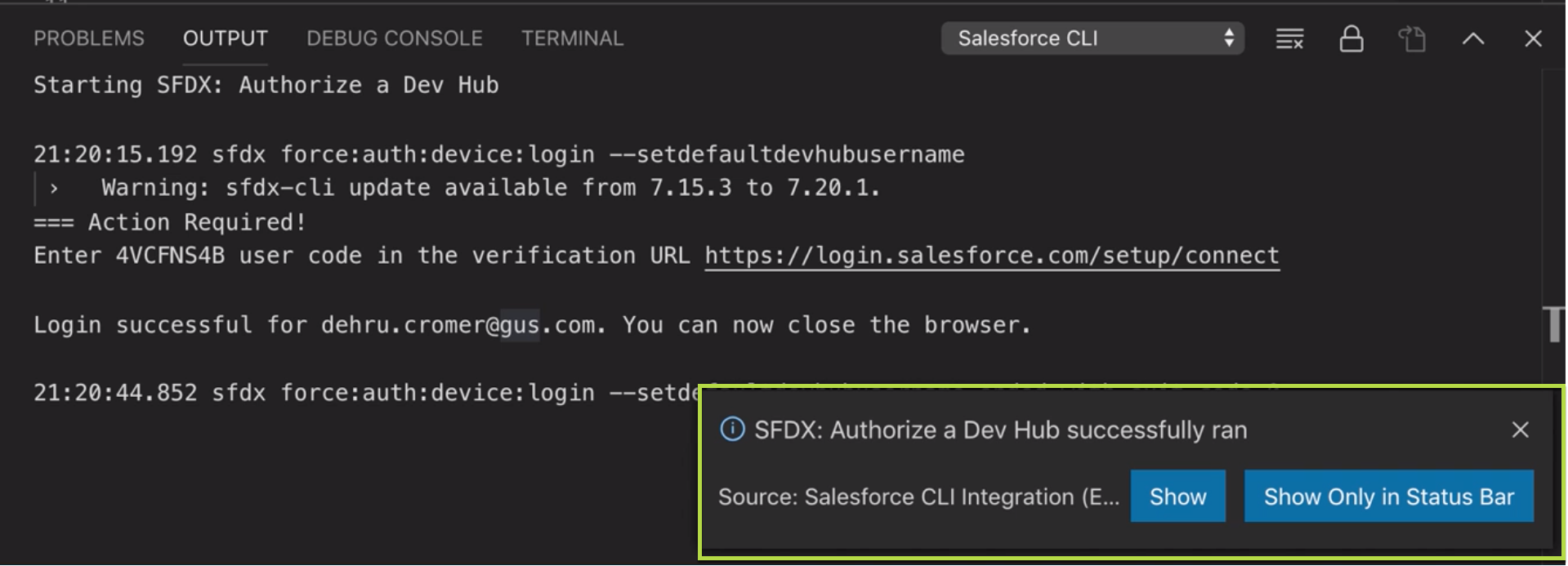
From the Command Palette, run the SFDX: Authorize a Dev Hub in the container. From the Output panel (below the editor region), you can get the user code and the verification URL required to complete the authorization.
If you are logged in to an org that you don’t want to authorize as a Dev Hub, make sure to log out. Otherwise, you're not prompted to enter the credentials for the org that you want to authorize. After the authorization is complete, the message
SFDX: Authorize a Dev Hub successfully ranis displayed. In case the success message is not displayed, check if you have the correct user code and try again. If the login page doesn’t prompt you to re-enter the code, terminate the command and run it again.
If you are interested, read more about Device Authentication Flow.
-
Run SFDX: Create a Default Scratch Org.
-
Click Reopen in Container to build a dev container. Now the side bar shows
Dev Container: Salesforce Project.You’ve set up a dev container for an existing project to use as your full-time development environment.
Follow these instructions for remote development using WSL 2.
First, set up WSL 2 on your machine. Follow the instructions provided by Microsoft.
Important: Only use WSL 2. There are known issues with WSL 1. These instructions assume Ubuntu. Other Linux distros should work, but the steps may be slightly different.
After you have installed WSL 2, set up your environment for Salesforce development. You need Node.js, Salesforce CLI, and OpenJDK.
To install Node.js, follow these instructions provided by Microsoft. We recommend that you use NVM to easily switch between node versions. For Salesforce development, use the LTS version of Node.js.
After Node.js is set up, install Salesforce CLI by running:
To install the JDK, run:
To determine the path of your JDK installation, run:
The output contains a path that looks something like /usr/lib/java-1.11.0-openjdk-amd64. Copy that path for later use.
-
Open an existing project or create a new project.
-
From the Command Palette, run Remote-Containers: Add Development Container Configuration Files. If you are unable to see this command, make sure that you have installed the latest version of the VS Code Remote Development Extension Pack.

-
Select Salesforce Project from the list of templates to add
SFDX .devcontainerfolder. The.devcontainerfolder contains thedevcontainer.jsonfile that defines how to configure the dev container and the extensions to install.VS Code detects the dev container configuration file and prompts you to reopen the project folder in a container. DO NOT RUN THIS YET.
-
Open the
.devcontainer/devcontainer.jsonfile and make these edits:- Remove the line
"dockerFile": "Dockerfile", - Set the value of
salesforcedx-vscode-apex.java.hometo the path you copied earlier after the commandupdate-java-alternatives --list.
- Remove the line
-
From the Command Palette, run Remote-Containers: Reopen in Container.
-
After the project is open, install the node modules. Open a new terminal in VS Code, which is mounted to the remote WSL environment, and run
npm i. -
Authorize orgs and create scratch orgs.
See Also (VS Code documentation):