Customization with Hooks
Hooks allow you to alter and extend the behaviour of existing Shopper API resources using the Script API.
Only existing customers can access some of the links on this page. Visit Salesforce Commerce Cloud GitHub Repositories and Access for information about how to get access to the Commerce Cloud repositories.
For more information on Script API, refer to the following documentation:
Resources can provide the following hooks:
before: Useful for custom validation, for example, if you're sending an address that you want to validate.after: Useful for changing data, for example: you're sending payment information that you need to verify with an external system and then persist it.modifyResponse: Allow you to modify what is contained in the response, for example: If there’s an attribute that you don't need or an additional attribute that you do need, you can use a response hook to modify what is obtained from an external system.
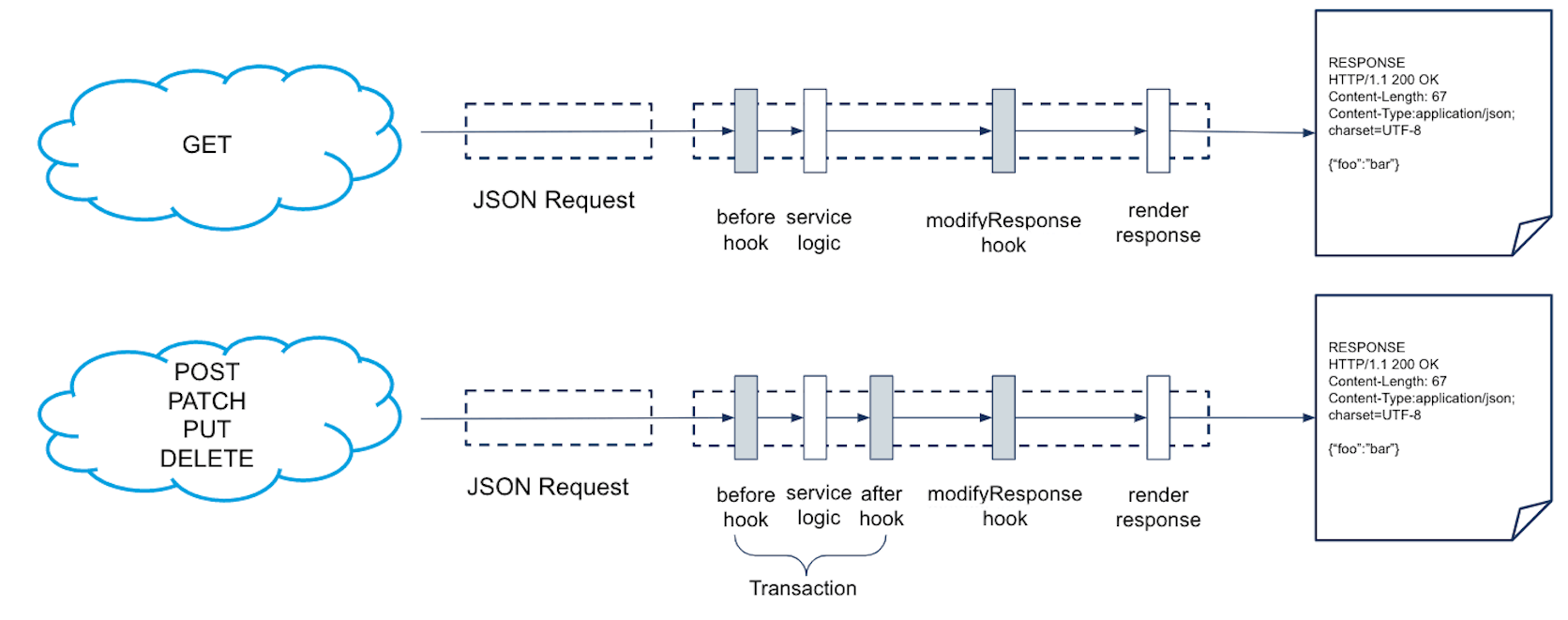
GET requests support before and modifyResponse hooks. State changing HTTP methods like POST, PATCH, PUT, and DELETE additionally support after hooks. The latter also writes transactions to the database accordingly.
Hooks don't apply to all Shopper APIs. For example, the Shopper Experience API provides its own customization capabilities for page and component types.
The Hook Method Details contains available hooks.
To use hooks for Commerce API, first enable it in Business Manager for your B2C Commerce instance.
Click App Launcher  and then select Administration > Global Preferences > Feature Switches and check Enable Salesforce Commerce Cloud API hook execution.
and then select Administration > Global Preferences > Feature Switches and check Enable Salesforce Commerce Cloud API hook execution.
To enable, you must have the Account Manager role of Business Manager Administrator for the instance.
- Place a
package.jsonfile in the top-level directory of your cartridge. - In the
package.jsonfile, define thehooksproperty to the path of thehooks.jsonconfiguration file. This path is relative to the directory containing thepackage.jsonfile: - In the
hooks.jsonfile, configure an array with the mappings of hooks to their script files with paths relative to thehooks.jsonfile: - For site specific use, register the cartridge to each appropriate site in Business Manager. To customize organization-level resources across all sites, such as libraries, register the cartridge to the Business Manager site.
Hook scripts are loaded as CommonJS modules. Hook functions must be exported. The exported name must match the name of the hook, without the package qualification. For example, the dw.ocapi.shop.basket.billing_address.beforePUT hook is exported as beforePUT:
For each hook your code MAY return a Status object to the server. If the status is OK, the server continues processing. If the status is ERROR, representing a handled exception, the server stops further processing, rolls back the transaction and responds with an HTTP 400 Bad Request fault. When an ERROR occurs, the server returns a fault to the caller, containing information like the error code, message, and details from the Status object. Uncaught exceptions in your code including the errors you throw cause an HTTP 500 Internal Error fault; in this case, the server rolls back the transaction.
Hooks for Shopper API extension points that return a value will SKIP the system implementation of the hook and any subsequent registered hooks for that extension point. To ensure the system implementation of a hook and any subsequent registered hooks for an extension point are not skipped, it is recommended that Shopper API hooks return nothing to allow important functions like the cart calculate hook to be executed.
Hooks for custom extension points will always execute all registered hook points regardless of their return value.
When an ERROR occurs, the server returns an RFC IETF rfc7807 ErrorResponse to the caller, containing information like the error code, message, and details from the Status object.
If your hook code does not return a Status object, multiple registered hook scripts might be executed, including the overridden base implementation. The Status object or value returned by these hooks will then be returned instead.
A single request can call multiple hooks. For example: adding a new payment instrument to a basket calls:
dw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.beforePOSTdw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.afterPOSTdw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.modifyPOSTResponse
To pass data between hooks, use request.custom. JavaScript objects added to the request are available in subsequent hooks.
For example, to call a 3rd party payment processor inside the transaction of adding a new payment instrument to the basket, you can make this call within the dw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.afterPOST hook (to ensure any errors rollback the transaction). After calling the payment service provider to initialize the payment request, you can return the relevant data to the client in the dw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.modifyPOSTResponse hook. To do this, add relevant data to the request.custom container to be handled by the modifyPOSTResponse hook.
As a result of many projects with customers, our community is maintaining a hook collection with many useful implementations to extend functionality or even provide new functionality. The hooks in the community collection cover a wide range of practical use cases.
For more information, check out the OCAPI Hooks Collection on the Salesforce Commerce Cloud GitHub repository.
The Calculate hook, dw.order.calculate, enables you to implement customized basket calculation logic. It can be used as the single place for basket calculation and recalculation. This hook provides a default implementation, which can be overridden.
The default logic of the following hooks implicitly call this hook:
- dw.ocapi.baskets.actions.afterMerge
- dw.ocapi.baskets.actions.afterTransfer
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.afterPATCH
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.agent.afterPUT
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.billing_address.afterPUT
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.coupon.afterDELETE
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.coupon.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.customer.afterPUT
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.gift_certificate_item.afterDELETE
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.gift_certificate_item.afterPATCH
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.gift_certificate_item.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.item.afterDELETE
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.item.afterPATCH
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.items.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.afterDELETE
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.afterPATCH
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.payment_instrument.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.price_adjustment.afterDELETE
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.price_adjustment.afterPATCH
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.price_adjustment.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.reference.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.shipment.afterDELETE
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.shipment.afterPATCH
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.shipment.afterPOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.shipment.shipping_address.afterPUT
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.shipment.shipping_method.afterPUT
- dw.ocapi.shop.basket.storefront.afterPUT
- dw.ocapi.shop.order.beforePOST
- dw.ocapi.shop.order.beforePUT
The following code snippet shows a sample call:
In this sample call, the parameters are:
"dw.order.calculate"- the extension point to call"calculate"- the script function to callbasket- the basket to be calculated
SiteGenesis uses the default implementation of the dw.order.calculate hook for basket calculation logic.
With B2C Commerce version 24.7, you can upload Shopper Context hooks at the site level by uploading a site-specific cartridge. When invoking site-specific hooks, you must provide a siteId.
If you do not provide a siteId, no error message is returned, but the site-specific hooks are not called. For details, see createShopperContext and updateShopperContext.
Using hooks with the B2C Commerce API (SCAPI) is similar to using hooks with OCAPI, but there are differences developers must be aware of. When you enable and maintain hooks, the same hooks are called for both SCAPI and the related OCAPI endpoints, so it’s possible to write a hook that is used for both. This is important if you use both API frameworks for your client applications.
Use request.isSCAPI() to determine SCAPI or OCAPI usage, especially if you’re already using the calculate hook in the context of controllers and use transactions in that hook, as that breaks SCAPI.
To add conditional behavior to a hook, use custom query string parameters. Parameters must be prefixed with c_:
SCAPI supports custom HTTP request and response headers for diagnostic and informational purposes.
- Custom headers must be prefixed with
c_. - Do not use custom headers to implement conditional behaviour, because custom headers are not considered when constructing a cache key. For details, see Server-Side Web-Tier Caching.
- Never use custom request headers in a way that affects the response body. Custom headers are only intended for diagnostic or informational purposes, such as logging.
The following example logs an error message for a required parameter value missing in the request header:
The following example provides a sample custom response header:
You can use SCAPI and OCAPI Hooks to implement custom validation logic to parse and handle errors.
For example, to use a hook to add custom validation of shipping addresses:
Use Status.addDetail(key, value) to add details to the error that the client can parse and use. For additional details, see Class Status.
If isValidAddress is false, SCAPI returns a HTTP 400 response with the content type: application/problem+json:
If your hook raises an unhandled exception or error (network error, code syntax error), then an HTTP 500 response is returned:
The Hook Circuit Breaker protects the system from excessive hook execution failures. If your hook generates too many errors, the circuit breaker is activated and returns an HTTP 503 response:
For more information, see Hook Circuit Breaker.
If a hook errors during processing, the request will fail. You can track hook errors with Log Center. Configure a search using the LCQL query category: ( com.demandware.wapi.servlet.ShopRestServlet ) AND stackTrace: ( HookInvocationException ). Alternatively, use the Correlation ID associated with the failing request.
All SCAPI responses must be returned within a specified timeout period. including the execution of any hooks that are applied. For details, see Timeouts and Limits.
For details on timeout value errors, see Error Response Codes.
modifyResponse hooks are a powerful way to create a response that best fits the needs of the application. You can add additional information to objects, or provide a more UI-friendly property set to improve the consumption on the client application.
Additional properties must be added only as custom properties (c_ properties).
When you enable caching for endpoints that use SCAPI hooks, the hook logic is executed by the application server and the result is cached. Neither the application server logic nor custom hook logic is executed again until the object expires from the cache. For details, see Server-Side Web-Tier Caching.
Basket calculations built into the B2C Commerce backend are enabled for determining basket information. SCAPI endpoints allow the manipulation of tax information on the basket.
With B2C Commerce 24.5, the following endpoints are supported with hooks enabled:
/checkout/baskets/{}/taxes/checkout/orders/{}/taxes/checkout/baskets/{}/items/{}/taxes
The following Script API methods are available to support the SCAPI external taxation APIs with hooks:
- dw.order.LineItemCtnr#isExternallyTaxed: Returns
trueif the basket was created withtaxMode = external. - dw.order.TaxMgr#applyExternalTax: Applies externally set tax rates to the given basket. Use when
dw.order.LineItemCtnr#isExternallyTaxedreturnstrue.
The following endpoint is not supported with hooks enabled. Calling this endpoint with hooks enabled results in a HTTP 409 error response from the request.
/checkout/baskets/{basketId}/price-books