Set Up Your Development Environment for Agentforce DX
Setting up your Agentforce DX environment is similar to setting up your Salesforce DX environment but with a few agent-specific extras. If you're already a Salesforce pro-code developer, you've probably completed most of these tasks or are familiar with them.
The pro-code tools for creating and testing agents are Visual Studio Code (VS Code), Agentforce Vibes IDE, and Salesforce CLI. VS Code is an integrated and extensible development environment (IDE) and consists of a code editor, build automation tools, a debugger, and intelligent code completion. Agentforce Vibes IDE is a web-based version of VS Code that you can use when you want to run VS Code inside a web browser.
Salesforce VS Code extensions are available from both the VS Code Marketplace and the Open VSX Registry, which you can use if you prefer using open-source projects. If you're using Agentforce Vibes IDE, you must install extensions from the Open VSX Registry.
You install Salesforce CLI and VS Code locally on your computer. Agentforce Vibes IDE is pre-installed with the Salesforce extension pack and Salesforce CLI. To set up Agentforce Vibes IDE, see Set Up Agentforce Vibes IDE.
-
Install the Agentforce DX VS Code extension from either the VS Code Marketplace or the Open VSX Registry.
The Agentforce DX extension depends on these VS Code extensions which are automatically installed if they're not found:
- Agent Script
- Apex and the Apex Replay Debugger
-
Install the Salesforce Extensions for Visual Studio Code from either the VS Code Marketplace or the Open VSX Registry.
The Salesforce Extension Pack includes tools for developing on the Salesforce platform, such as features for working with development orgs (scratch orgs, sandboxes, and DE orgs), Apex, Lightning web components, Aura components, Visualforce, and SOQL. The extension pack also includes Agentforce Vibes.
-
Install Salesforce CLI on your computer.
-
Open VS Code.
-
From VS Code's integrated terminal, run the
sf searchCLI command and enteragentto view the available agent-related commands.A summary of the command appears at the bottom as you use the arrow keys to scroll through the list.
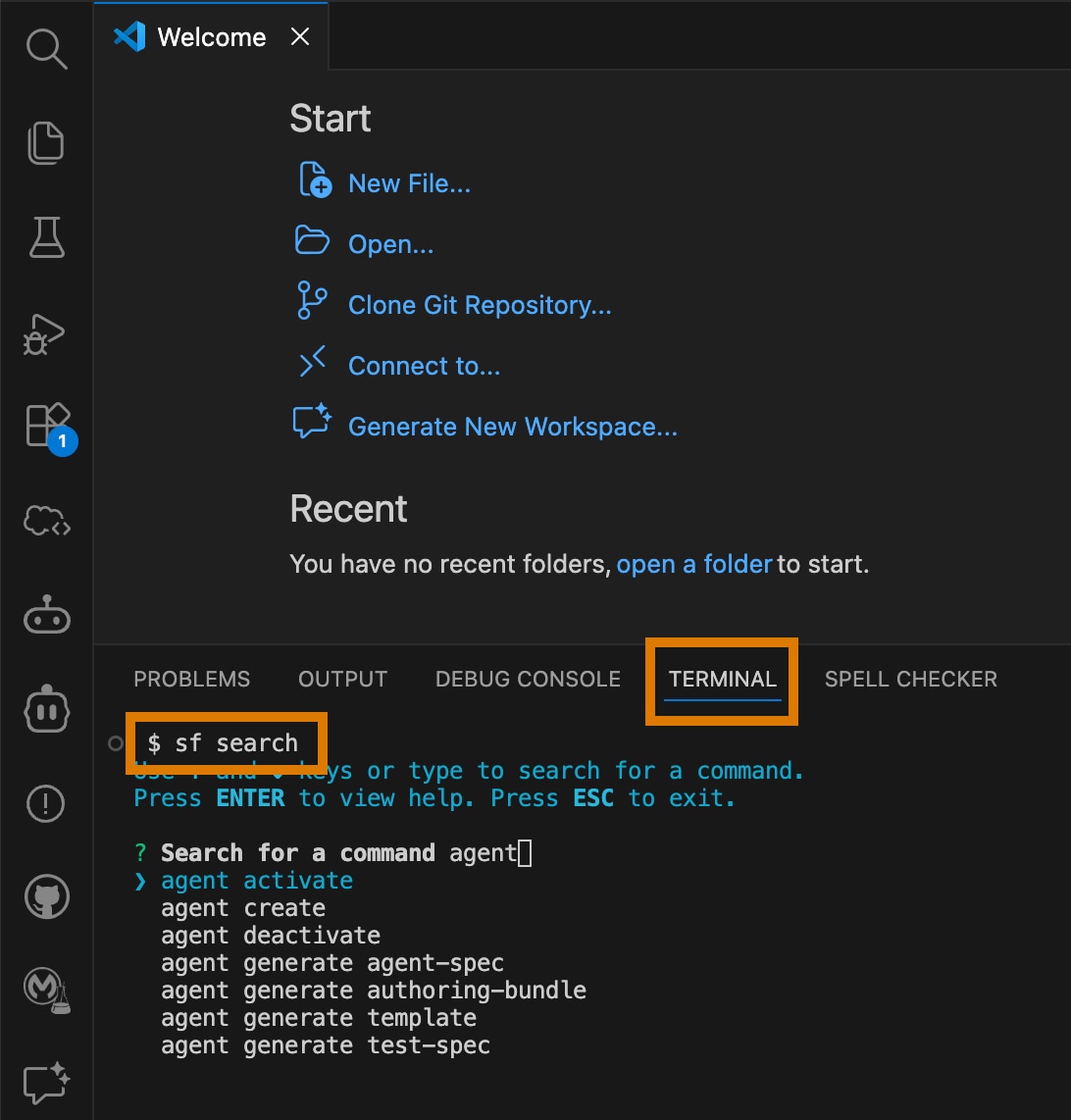
You can also run Salesforce CLI commands from a separate terminal (macOS, Linux) or command prompt (Windows) if you prefer.
-
To view detailed information about a particular command, such as its flags and examples of how to use it, use the
-–helpflag. Use-hfor concise information.
If you’re new to pro-code development using VS Code, check out the Trailhead badge Quick Start: Visual Studio Code for Salesforce Development.
You can use either a sandbox or scratch org for Agentforce development, but it’s important to understand the capabilities and limitations of each. You can also use a Developer Edition org that has Agentforce and Data 360 enabled.
You can use both sandboxes and scratch orgs to develop and test agents, code, and other configuration changes without compromising the data and applications in your production org.
Sandboxes are copies of your Salesforce production org. They contain all the metadata that was in your org at the time they were created. Developers often use Developer and Developer Pro sandboxes, because they can be refreshed often, which brings in new changes from your production org. Partial and Full Copy sandboxes are useful for integration and user testing because they contain data from your production org in addition to the metadata, although this ability restricts how often Partial and Full Copy sandboxes can be refreshed.
Scratch orgs are empty environments that don’t have any metadata or data from your Salesforce production org, so you can create them quickly. Scratch orgs are ideal for source-driven development where you externalize all the metadata from your production org, then deploy the metadata to the scratch org when you want to work on a specific part of your application.
To select the appropriate developer environment, consider whether your agents require access to Agentforce Data Libraries and Data 360:
- No Data Libraries Required: Use scratch orgs configured for Agentforce development.
- Data Libraries Required: Use a sandbox org capable of connecting to Data 360.
Combining Data 360 and Agentforce is the best way to create successful agents. For that reason, we recommend that you work in a sandbox when using Agentforce DX. Developer and Developer Pro sandboxes are ideal choices. See Choose the Right Salesforce Org for the Right Job for a deeper dive into the available choices.
To create a sandbox, use one of these two methods:
- Salesforce CLI: Run the
org create sandboxcommand. See Sandboxes in the Salesforce DX Developer Guide. - Setup UI in your org. See Create, Clone, or Refresh a Sandbox in Salesforce Help.
To create a scratch org, run the org create scratch Salesforce CLI command. See Scratch Org Access for details about creating a scratch org definition file that automatically enables Einstein and Agentforce, which you need to use the agent commands.
Newly-created scratch orgs can take some time to be fully set up with Einstein and Agentforce features. If you encounter errors about the LLM or agents not being provisioned when immediately running agent create or agent generate spec after creating a scratch org, wait a moment and try again.
Use this form to sign up for a free Salesforce Platform environment with Agentforce and Data 360.
Although sandboxes are a copy of your production org, some additional manual configuration is required after the sandbox is created to enable Agentforce in it. If you use a Developer Edition org, follow these steps to ensure that it's ready for Agentforce DX.
-
Log in to your sandbox or Developer Edition org.
-
If your agents don’t require Data 360, skip to the next step. If your agents require Data 360, turn on Data 360.
-
From Setup, find and select Data Cloud Setup Home.
-
Follow the directions in Turn On Data 360.
Data 360 setup can take up to 60 minutes to complete; the Setup page lets you know when it's finished.
Don’t continue to the next step until Data 360 setup has fully completed.
-
-
From Setup, find and select Einstein Setup.
-
Make sure that Einstein is enabled. If not, select Turn on Einstein.
-
Reload the Setup UI.
If you just enabled Einstein for the first time, reloading Setup is required so that Agent setup becomes available.

-
-
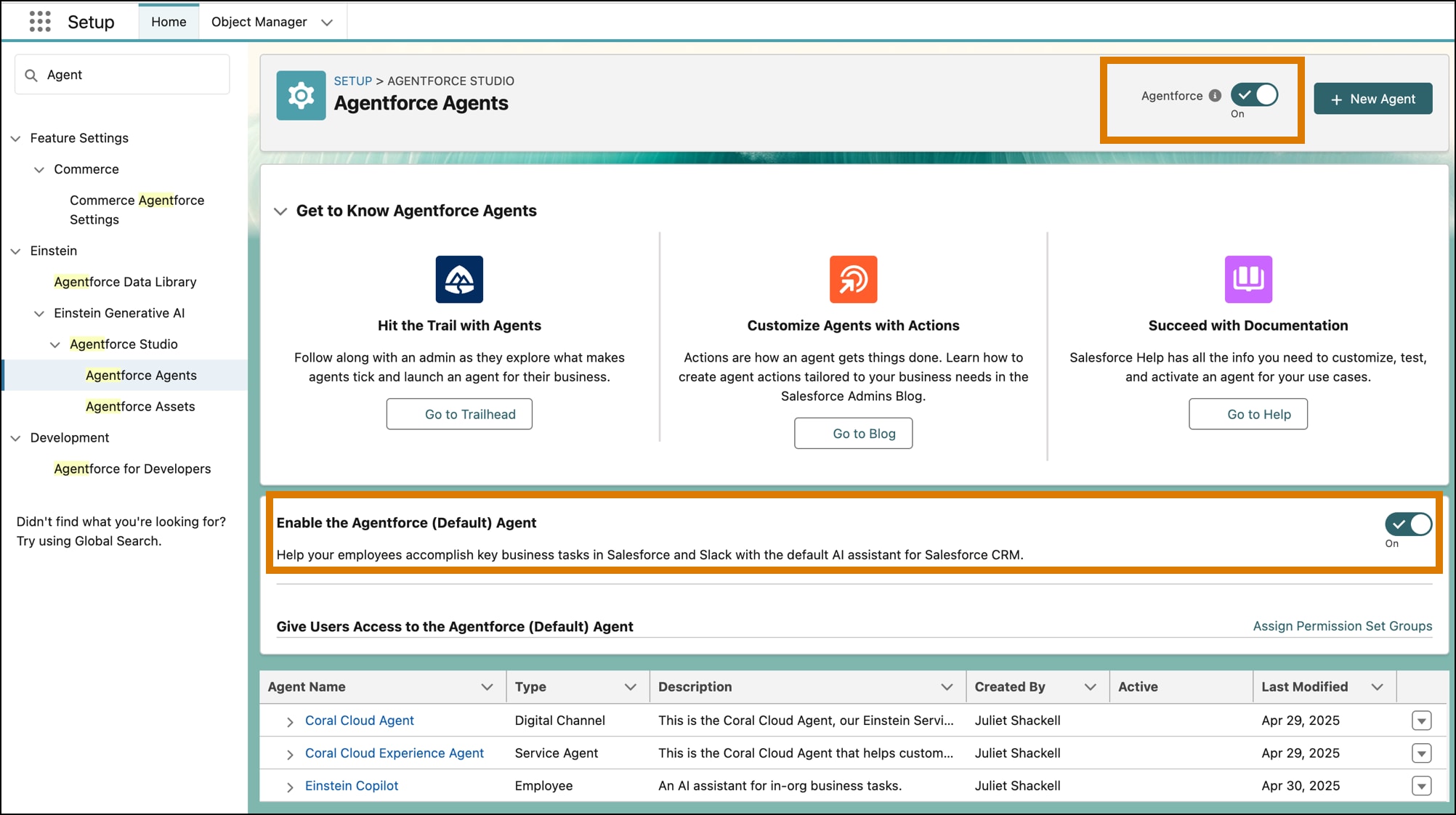
From Setup, find and select Agentforce Agents
- Select Agentforce.
- Select Enable the Agentforce (Default) Agent.
A Salesforce DX project provides a project structure for your org’s metadata (code and configuration), sample data, and all your team’s tests. Development teams store these items in a version control system, such as GitHub. Agents are like any other Salesforce customization in that they’re made up of metadata, so you still use DX projects to store and work with them.
- Open VS Code, click View | Command Palette, and then select SFDX: Create Project.
- Select Standard (Standard project template default).
- Enter a name for your project, such as
agentforcedx. - Navigate to the location where you want to create the project, then click Create Project.
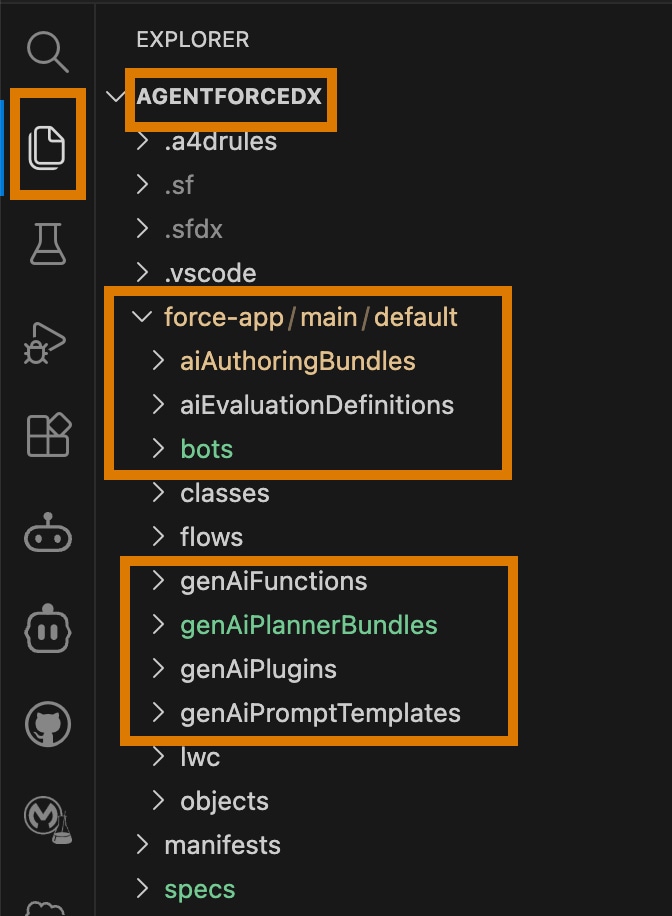
A standard Salesforce DX project opens in VS Code's Explorer. The following screenshot highlights the agent-related metadata directories in the DX package directory.
New DX projects don't automatically include the highlighted metadata directories, but as you start authoring and testing your agents, your project will soon include them.
If you want to run Salesforce CLI commands directly in the integrated terminal, or from a separate terminal (macOS, Linux) or command prompt (Windows), here are the equivalent commands for setting up a Salesforce DX project:
Authorize your sandbox or developer edition orgs so you can work in them with VS Code and the CLI commands.
- In VS Code, click View | Command Palette and then select SFDX: Authorize an Org.
- Click Project Default.
- Enter an alias for your org, such as
agentforce. - In the browser window that opens, sign in to your org with your login credentials.
- Click Allow, which allows Salesforce CLI to access your org.
- Close the browser window. Your org is now authorized and set as your default org.
Here’s the equivalent Salesforce CLI command that you can use in VS Code’s integrated terminal. Or run it in a separate terminal (macOS, Linux) or command prompt (Windows) from within your DX project.
- Trailhead: Quick Start: VS Code Development for Salesforce Development
- Salesforce CLI Setup Guide: Install Salesforce CLI
- Salesforce Extensions for Visual Studio Code
- Salesforce DX Developer Guide: Project Setup
- Salesforce DX Developer Guide: Authorization
- Salesforce CLI Command Reference: agent Commands
- Salesforce CLI Command Reference: org Commands
- Salesforce Help: Design and Implement Agents