Build Lightning Web Components and Flows with Models API
You can use the Models API Apex classes to build Lightning web components (LWCs), flows, and other applications that have access to any of the capabilities of the Models API. This feature opens up many use cases that take advantage of generative AI and the Einstein Trust Layer. Use this page to get started with some sample implementations.
These examples are meant to demonstrate what you can do with the Models API. They’re not intended as production-quality code samples.
These examples use the Models API Apex classes. Review how to use these Apex classes before proceeding.
For the Lightning web component (LWC) examples, ensure that you’re familiar with building LWCs.
- Trailhead: Lightning Web Component Trail
- Lightning Web Components Developer Guide: Get Started with Lightning Web Components
- Lightning Web Components Developer Guide: Calling Apex Methods
- Lightning Web Components Developer Guide: Call Apex Methods Imperatively
For the Flow Builder examples, ensure that you’re familiar with building Flow Builder actions.
- Salesforce Help: Automate Tasks with Flows
- Salesforce Help: Let Flows Execute Apex Actions
- Apex Developer Guide: InvocableMethod Annotation
- Trailhead: Flow Builder Trail
The best way to get started building Lightning web components that access the Models API is to check out our Trailhead module: Get Started with the Models API.
This video shows you how to build a Lightning web component that accesses the Models API, using one of the examples on this page.

This example shows you how to build a simple component that takes a prompt, calls the Models API Generate Text capability, and passes back the generated response.
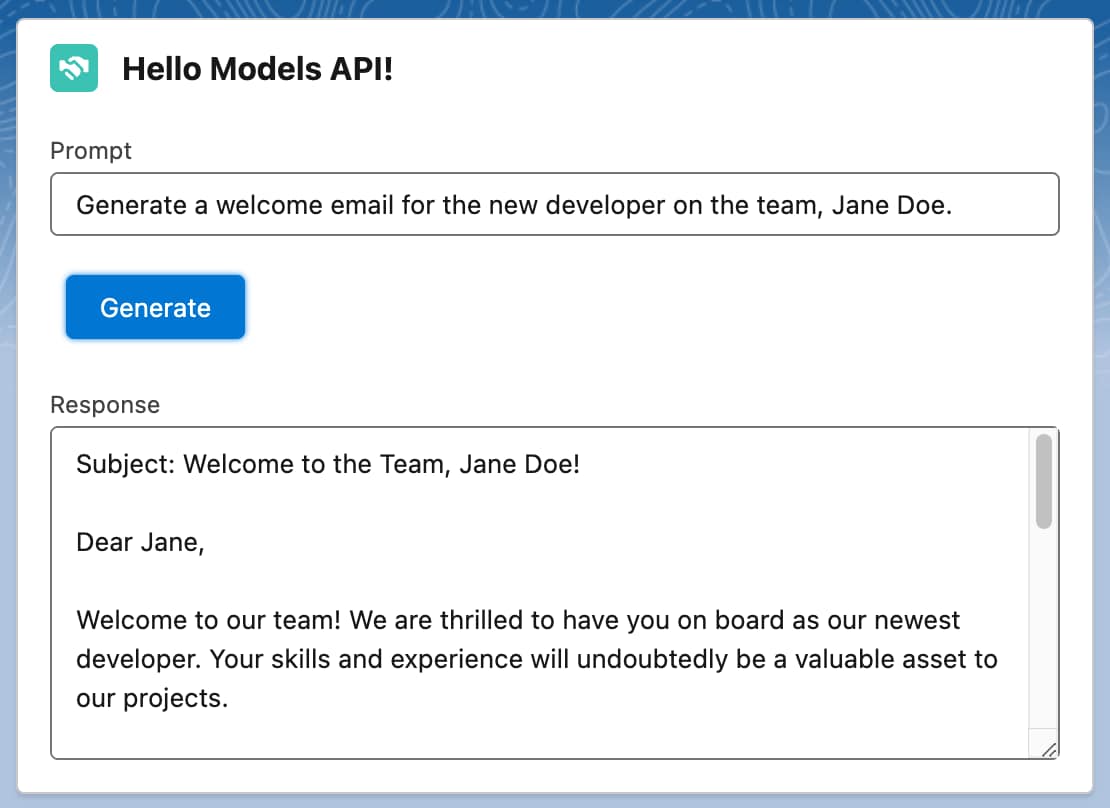
This Apex code takes a prompt as input and returns a response from the createGenerations method. You need to add this Apex code to your org so that you can call the code imperatively.
This HTML code presents a simple UI that contains an input field for the prompt, a button to generate the text, and an output field for the response.
This JavaScript code handles the button click event and makes a request to the Apex method.
This example shows you how to build an Apex invocable action compatible with Flow Builder that takes a prompt, calls the Models API Generate Text capability, and returns the generated response.
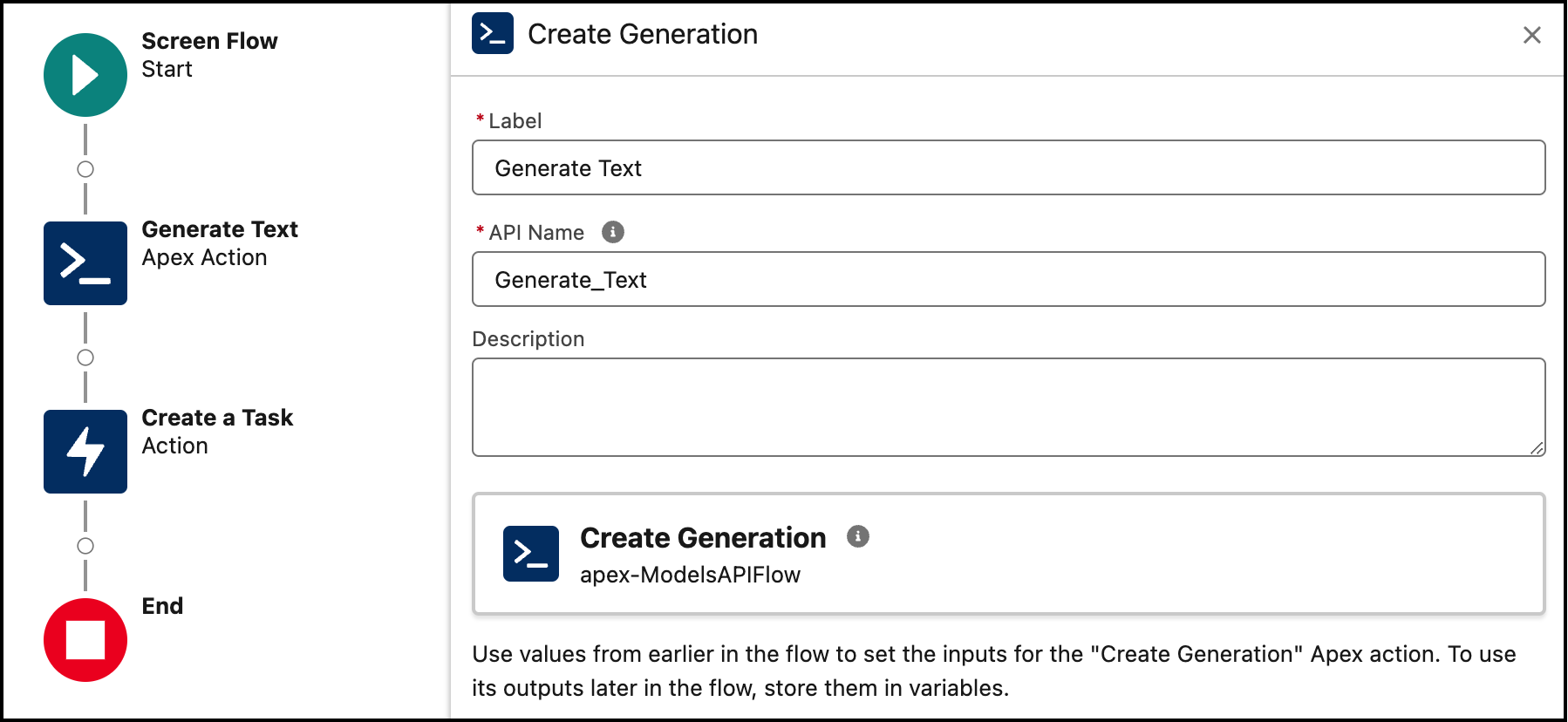
This Apex code takes a prompt as input and returns a response from the model. It uses the @InvocableMethod annotation so that it can be accessed from Flow Builder.
This example shows you how to use the Models API Generate Chat capability to build a component that takes a system prompt and a user prompt and produces a response. This example allows you to experiment with various prompt engineering patterns, such as chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting.
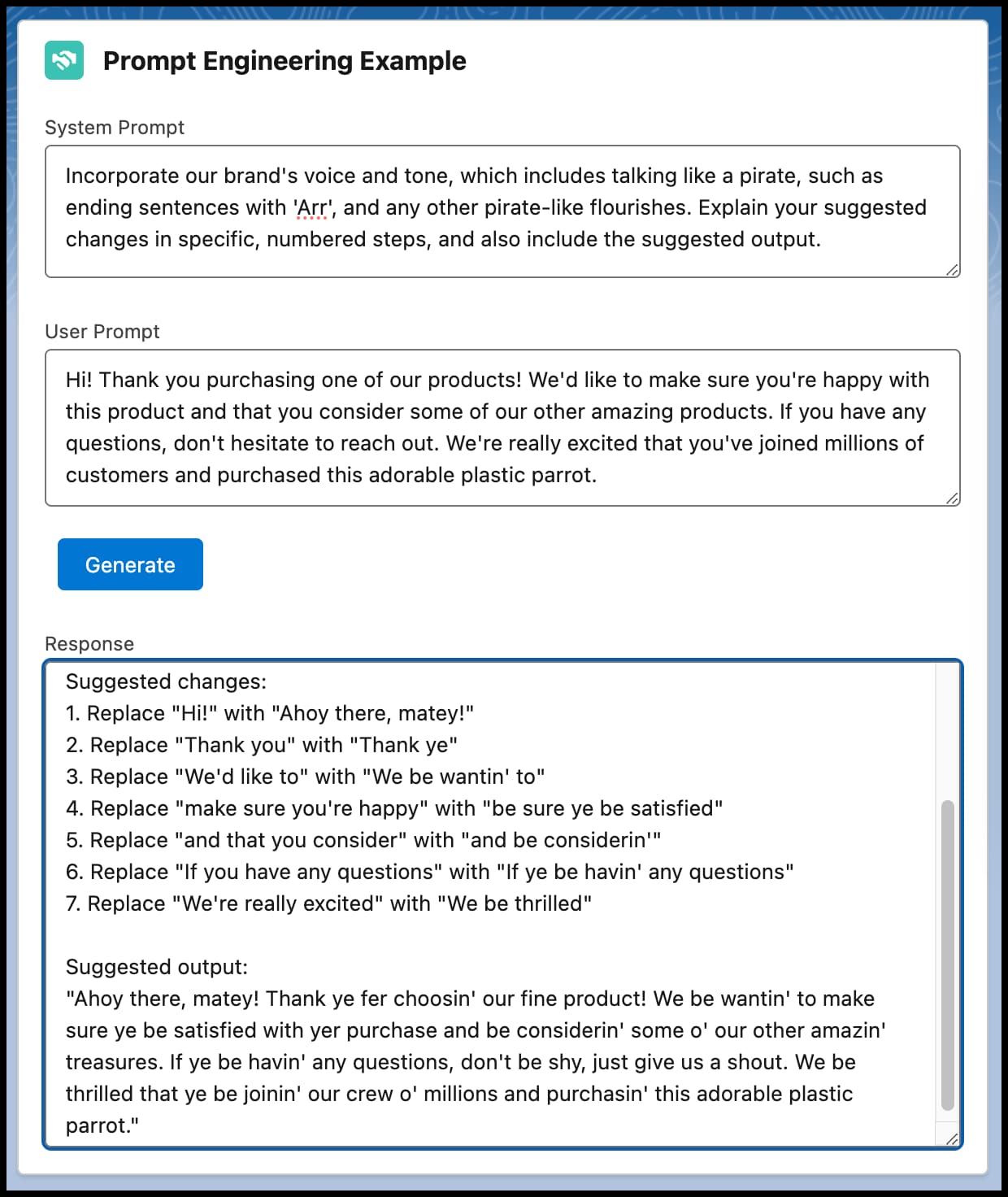
This Apex code takes the system and user prompts and calls the Generate Chat capability of the Models API.
This HTML code contains the user interface for the prompts and the response.
This JavaScript passes prompt information to the Apex code.
This example shows you how to build a simple chat component that uses the Models API Generate Chat capability to build a chat interface.
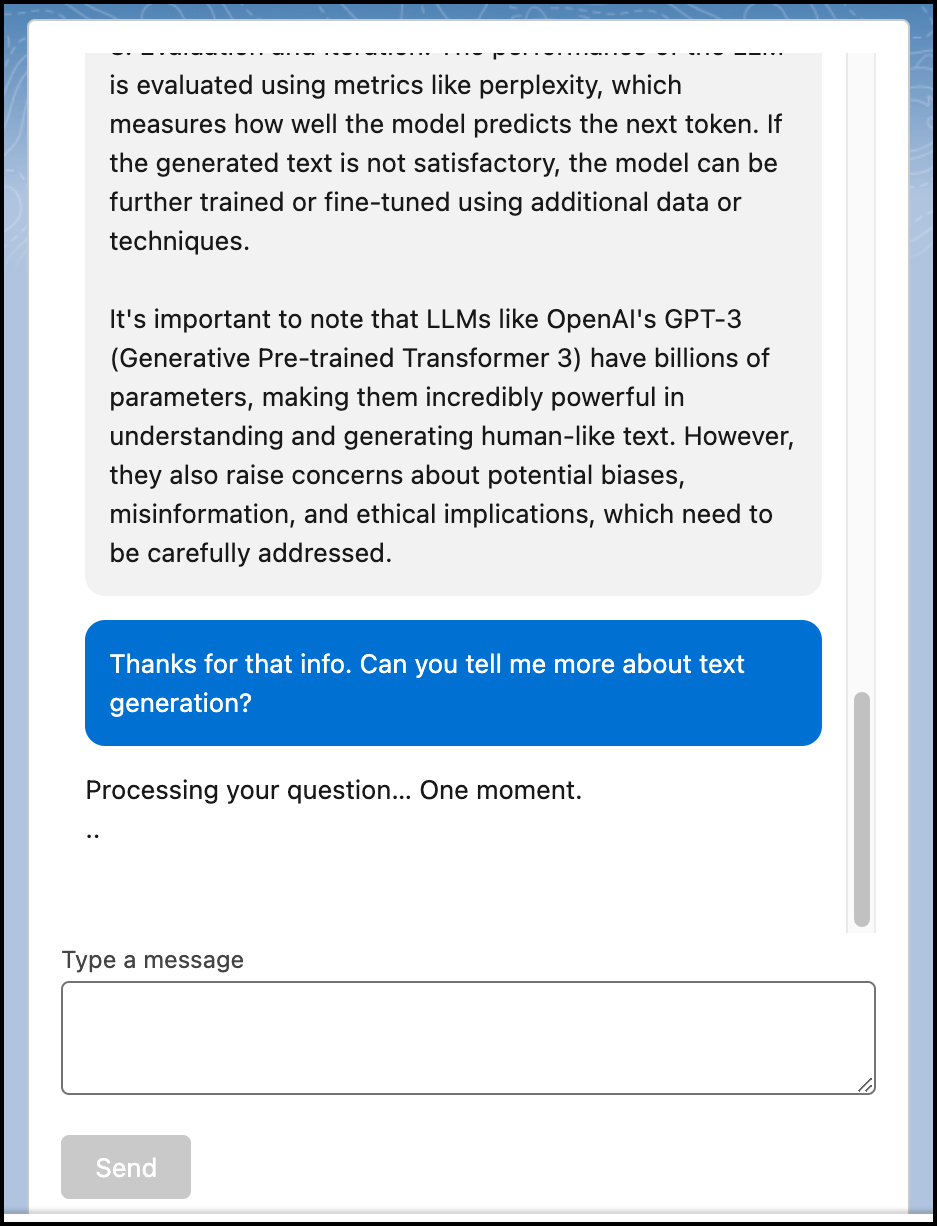
This Apex code parses the chat input messages and calls the Generate Chat capability of the Models API.
This Apex class holds information about a chat message.
This HTML code contains the user interface for the chat component.
This JavaScript passes user interface information to the Apex code.
This CSS code styles the user interface to look like a chat experience.
- Models API Developer Guide: Access Models API with Apex
- Trailhead: Get Started with the Models API