Appearance
Exercise 1: Ingest Contacts Using the CRM Connector
In this exercise, you’ll ingest Salesforce CRM data into Data 360 using the Salesforce CRM connector, and review how it maps into the Customer 360 Data Model.
Step 1: Verify that Data 360 is provisioned
Before you begin, confirm that Data 360 is provisioned in your org.
Open the Setup Menu, then select Data Cloud Setup.
Check which screen you see:
Option A — Already provisioned (you can continue):
If you see Your Home Org Details, provisioning is complete. Continue to Step 2.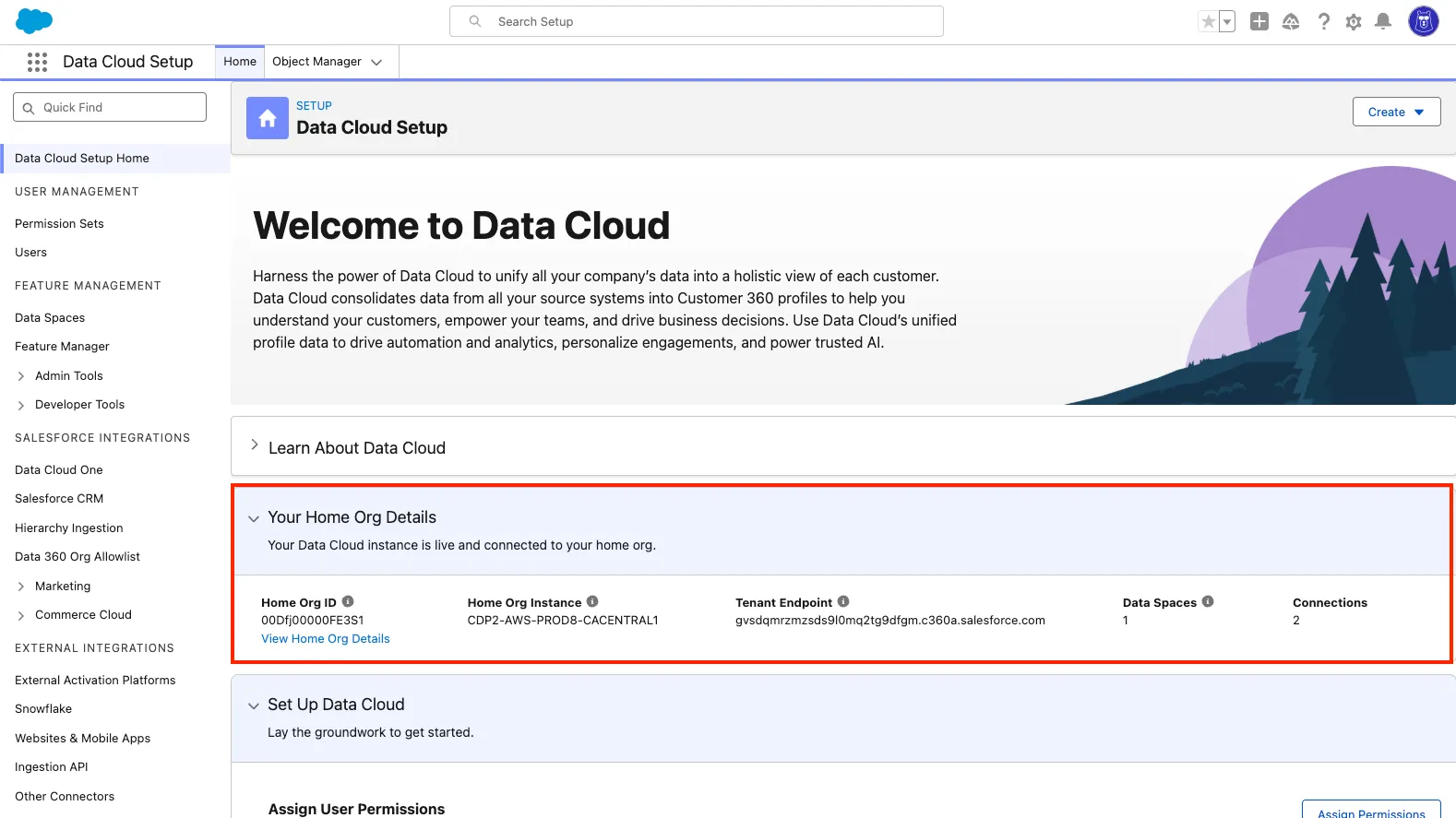
Option B — Not provisioned yet (you must provision):
If you see Set up Data Cloud, your org still needs provisioning.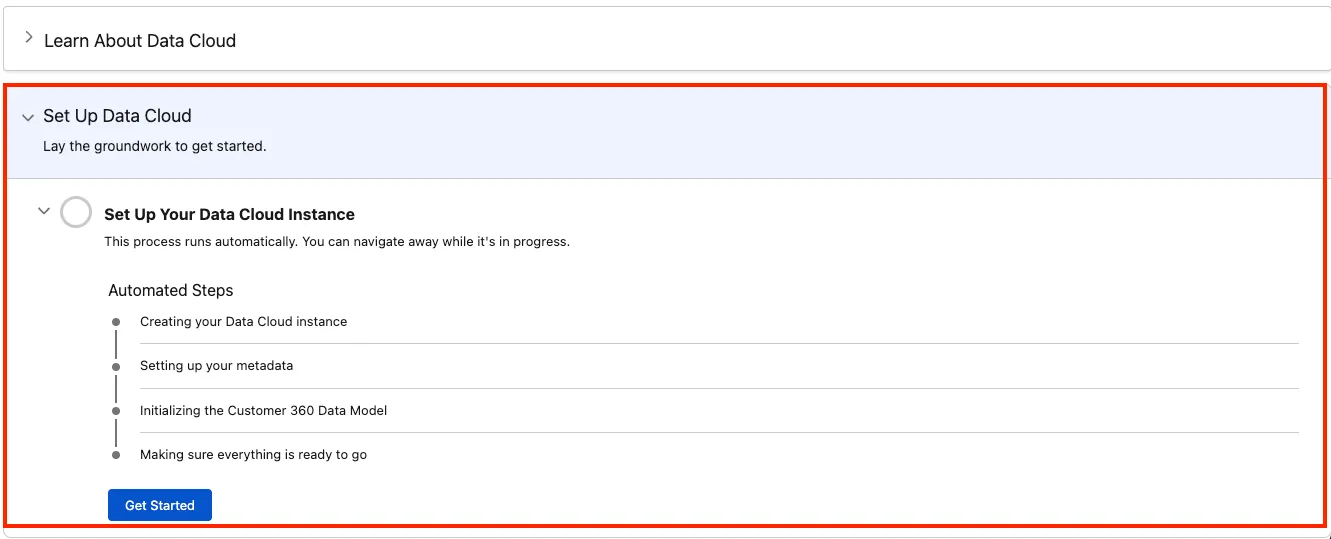
Click Get Started to begin provisioning. This can take 30–45 minutes.
TIP
If you start provisioning, wait until it finishes before continuing to Step 2.
Step 2: Create the Contact data stream using the Salesforce CRM Connector
In this step, you’ll ingest Salesforce Contact records into Data Cloud using the Salesforce CRM connector.
Using the App Launcher, open the Data Cloud application.
Click the Data Streams tab.
Click New.
Under Connected Sources, select the Salesforce CRM connector, and click Next.
Select the Sales object bundle, and click Next.
TIP
Using an object bundle helps you ingest a related set of objects together. For the Sales bundle, you’ll see standard fields and relationships for Account, Contact, Lead, Opportunity Contact Role, and User.
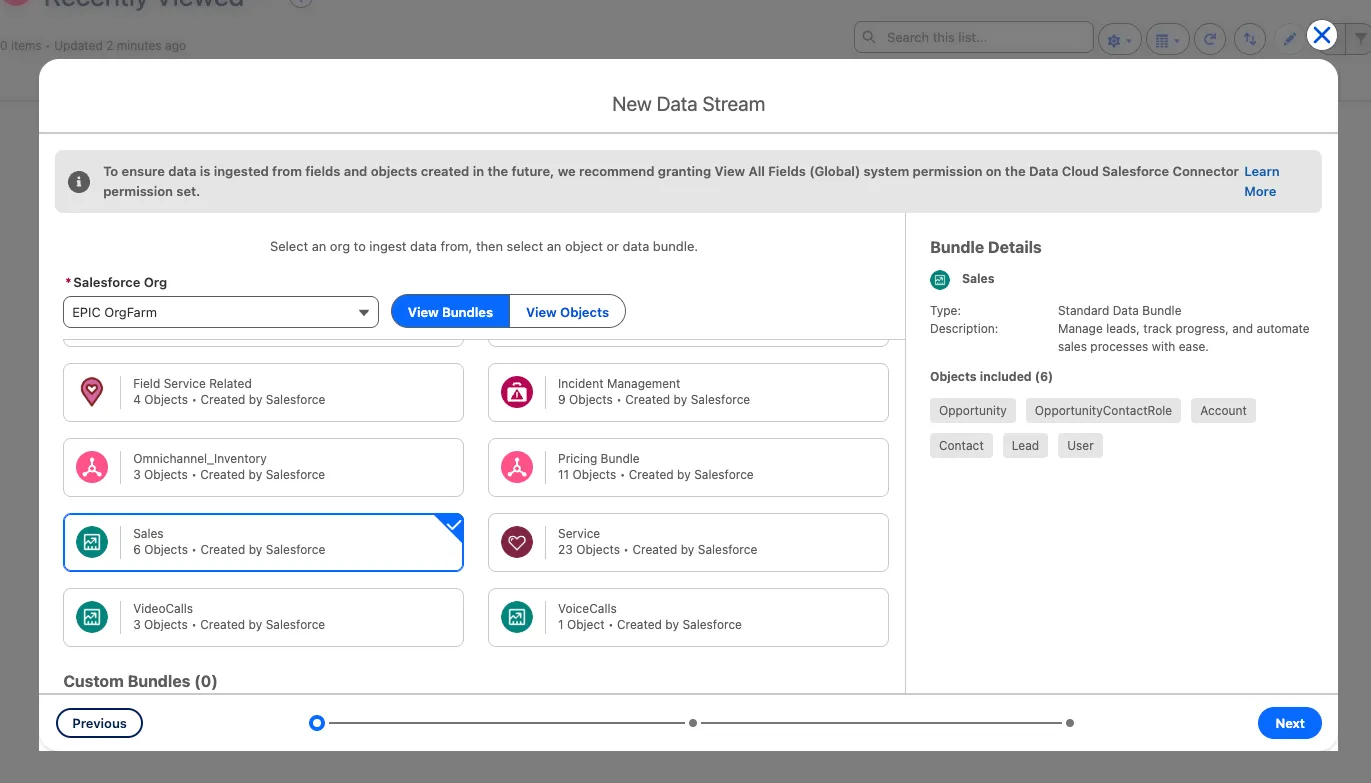
Review the fields being imported, and click Next.
Leave the default data space selected, and click Deploy. This can take up to 5 minutes.
Click the Data Lake Objects tab, and notice that a Contact_Home data lake object (DLO) has been created.
Click the Contact_Home DLO, and notice all the fields of the Salesforce Contact object.
Step 3: Review the mappings
In Data 360, you map data lake objects (DLOs) to a standardized data model known as the Customer 360 Data Model. This canonical data model ensures consistent representation of the data, regardless of its origin. Mapping data to a common data model facilitates data unification, and makes it easy to access and act on data from various sources in a consistent way.
Many organizations store Contacts in Salesforce and other customer data in external systems (for example, files in Amazon S3). These systems represent individuals in different ways. For example, one system might use a field called “Surname” while Salesforce uses “Last Name”.
Data 360 abstracts these differences by mapping data to the Customer 360 Data Model, which includes a generic Individual object. In this workshop, you’ll map multiple sources to a shared set of Customer 360 entities.
To review the mappings of the Contact DLO to the Customer 360 Data Model:
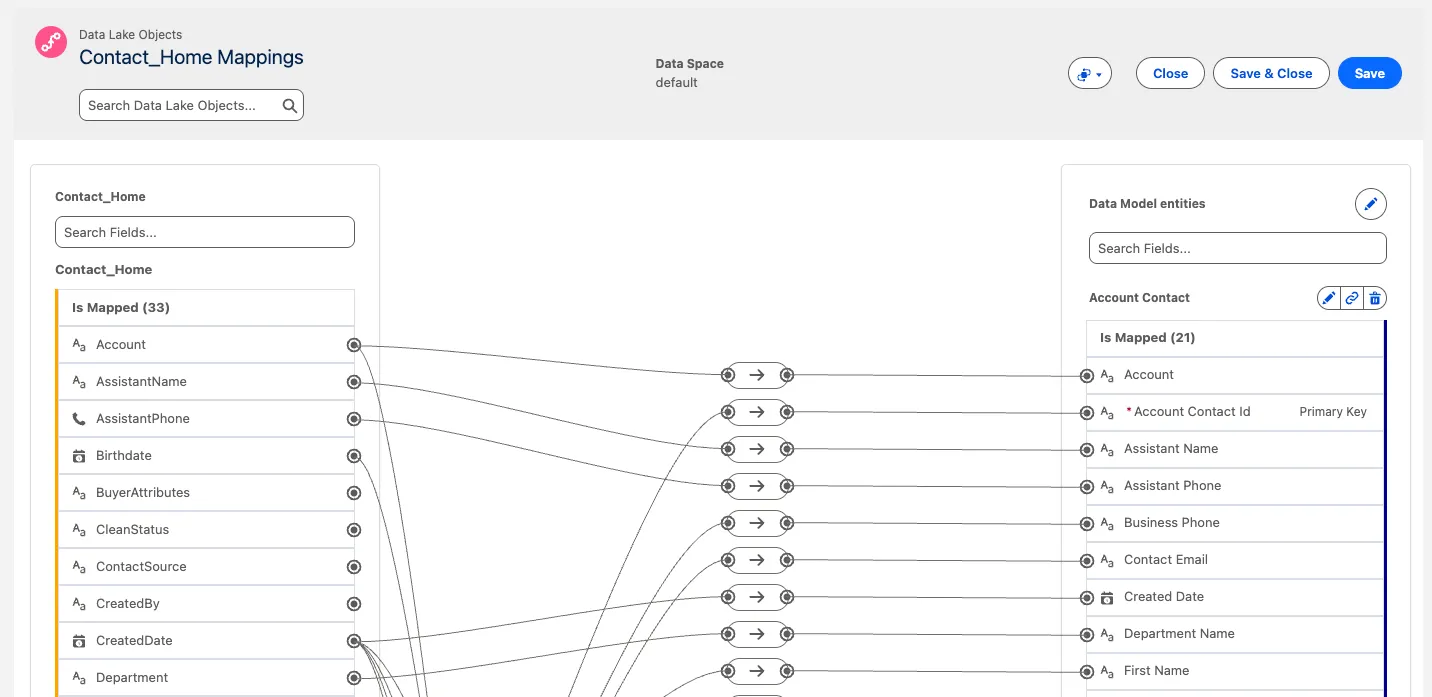
From the Contact_Home data lake object, click the Review button in the Data Mapping panel on the right.
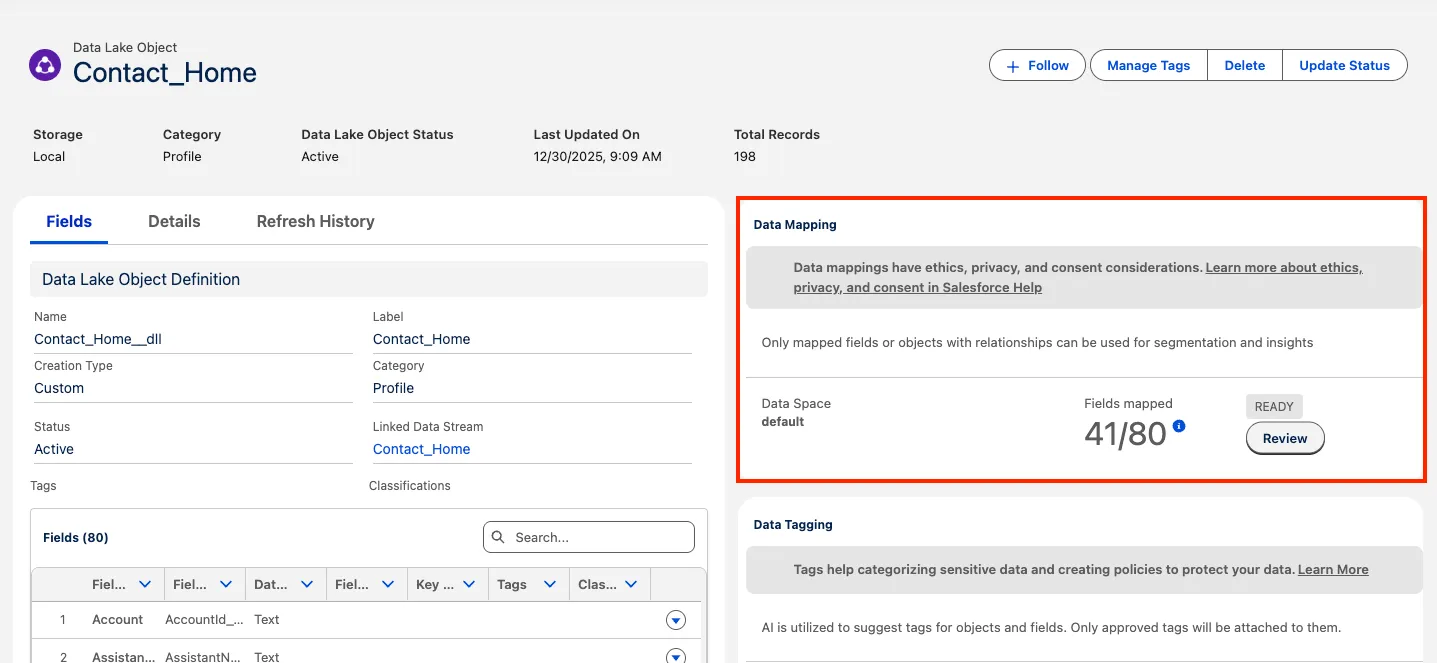
Review the mappings:
Review the Source object on the left-hand side: these are the fields of the Salesforce Contact object that you ingested into a data lake object (DLO).
Review the Destination objects on the right-hand side: these are standard entities within the Customer 360 Data Model, also known as data model objects (DMO). Note that your Contact DLO is mapped to five DMOs: Account Contact, Contact Point Address, Contact Point Email, Contact Point Phone, and Individual.
Summary
In this exercise, you validated Data 360 provisioning, ingested Salesforce Contacts using the CRM connector, and reviewed how the Contact data lake object maps to the Customer 360 Data Model.